Study in Japan
Don't know what to do?
Get Free Counselling
Study in Japan – Everything You Need to Know
For Canadian students looking for an international education, Japan is an appealing option because of its respected universities, advanced research, and distinct culture. If you are considering studying in Japan, here’s what you should know about the process, mainly concerning student visas.
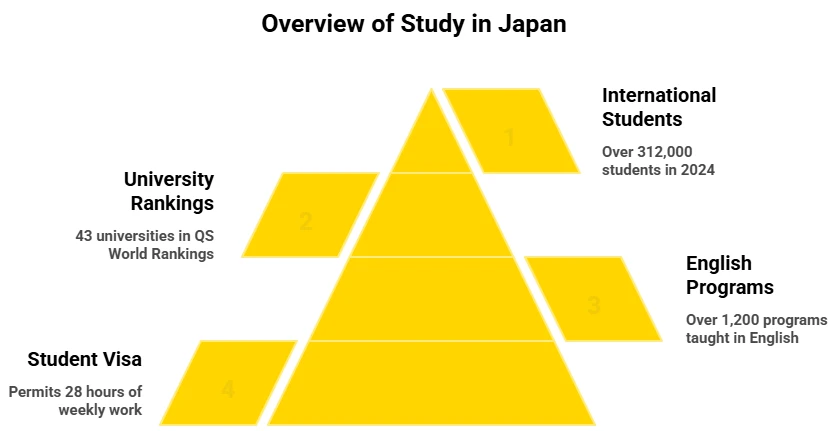
- In 2024, Japan hosted over 312,000 international students, and this number is projected to increase in 2025 (JASSO).
- 43 Japanese universities are listed in the QS World University Rankings for 2025.
- There are more than 1,200 programs taught in English, which can be a plus for students from Canada.
- The average yearly tuition at public universities is about ¥535,800 (roughly CAD 4,900).
- With a student visa, students are permitted to work up to 28 hours each week.
*Want to study in Japan? Sign up with Y-Axis for comprehensive support with the process.
What is a Japan Student Visa?
A Japan Student Visa serves as the official document for international students who want to reside and study in Japan for more than 90 days. This visa is needed for enrollment in educational institutions like universities, language schools, vocational colleges, or research programs.
The process starts with getting accepted into a Japanese institution that's recognized. Once admitted, students must obtain a Certificate of Eligibility (CoE) from the Japanese Immigration Bureau. With the visa, students can attend school full-time and work part-time, up to 28 hours each week, to help pay for their stay in Japan.
Why Study in Japan?
Some of the reasons why Japan should be your preferred destination for study abroad are given below.
- Opportunities for study at well-regarded universities and involvement in advanced research.
- Tuition costs are relatively low when compared to other G7 nations.
- A lively culture that mixes traditional elements with modern advances.
- The chance to learn Japanese, which can help with international career options.
- Options for graduates to get work visas after they finish their studies.
Benefits of Studying in Japan
The benefits of studying in Japan are given below.
- Degrees are of good quality and are known around the world.
- Many scholarships are available for students from other countries.
- The living environment is safe and clean, and public transport is good.
- There are many chances to experience the culture and learn the language.
- Students can work part-time to help pay for their living costs.
Types of Japan Student Visas
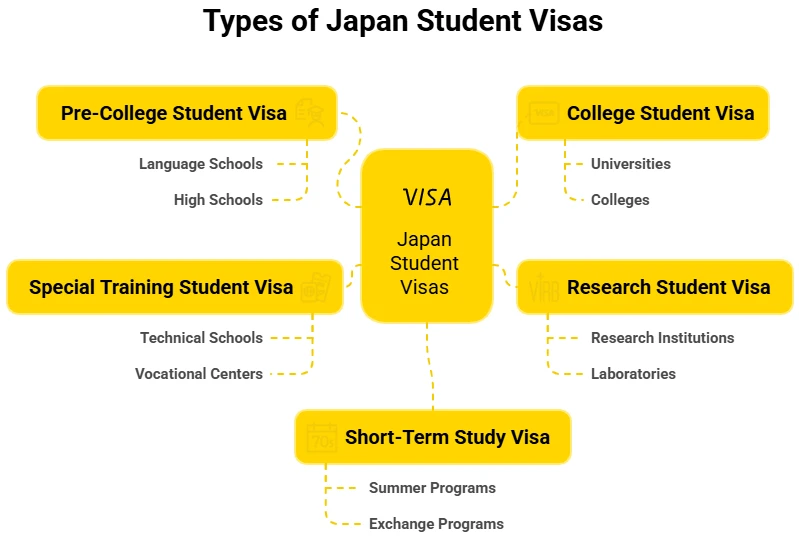
Japan offers various types of student visas to international students, such as:
- Pre-College Student Visa
- College Student Visa
- Research Student Visa
- Special Training Student Visa
- Short-Term Study Visa (less than 90 days)
Pre-College Student Visa
The Japan Pre-College Student Visa is for international students, including Canadians, who want to study in Japan at a level below university. This visa is often used by students going to high schools, language schools, or prep courses before they enter college.
- It can last up to 2 years, depending on how long your course is.
- To be eligible, students must be accepted into recognized Japanese schools that have pre-college programs.
- With a special permit from immigration, people with this visa can work part-time (up to 28 hours a week).
College Student Visa
The Japan College Student Visa serves students across the globe, and that includes Canadians, who gain acceptance into a higher learning institution like a university, grad school, junior college, or professional school in Japan. This visa lets students stay in Japan for their program, normally one to four years.
- To get this visa, you will need a Certificate of Eligibility (CoE) from the Japanese Immigration Bureau and evidence that you can pay for tuition and living costs.
- With student status, you can also seek permission to work part-time, up to 28 hours a week.
Research Student Visa
The Japan Research Student Visa allows international students, for example, those from Canada, to perform research or preparatory learning at a Japanese school without pursuing a degree. Students who intend to join a graduate program or work on particular research under a professor's guidance often use it.
- Depending on the research strategy, the visa is issued for six months to two years.
- A letter of invitation or acceptance from a Japanese school and a Certificate of Eligibility (CoE) are needed for the visa.
- With immigration approval, students with this visa can work part-time in Japan for up to 28 hours each week.
Special Training Student Visa
The Japan Special Training Student Visa allows international students, such as Canadians, to attend vocational schools or technical training programs in Japan. This visa suits individuals seeking focused skills or hands-on training in areas like design, culinary arts, healthcare, IT, and other specific industries.
- The visa's validity varies from 6 months to 2 years, based on the program duration.
- Applicants need acceptance into a recognized Japanese vocational school and a Certificate of Eligibility (CoE).
- With permission from immigration, students with this visa can work part-time, up to 28 hours per week.
Short-Term Study Visa (less than 90 days)
The Japan Short-Term Study Visa is designed for international students intending to study in Japan for under 90 days. It suits those attending language courses, cultural exchanges, seminars, or workshops not needing a long stay.
- This visa lasts up to 90 days and can't be extended within Japan.
- Applicants need to show proof of enrolment in a short course and enough money to support their time there.
- The Japan student visa holders cannot work part-time in Japan.
Eligibility Criteria for a Japan Student Visa
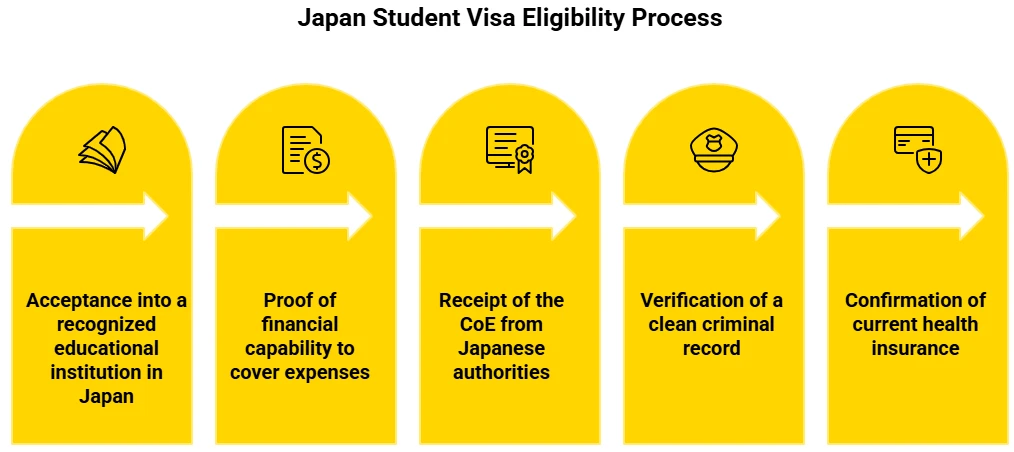
The eligibility criteria for a Japan student visa are given below.
- Admission to an accredited educational institution in Japan.
- Sufficient funding to bear tuition and living expenses (roughly ¥2 million annually).
- A Certificate of Eligibility (CoE) is granted by Japanese officials.
- A clear criminal history and current health insurance coverage.
Documents and Requirements for a Japan Student Visa
The documents required to apply for Japan student visa are given below.
- A valid passport
- The completed visa application.
- Your Certificate of Eligibility (CoE).
- An acceptance letter from your Japanese school.
- Financial records, like bank statements or sponsor letters.
- Passport-sized photographs.
Step-by-Step Process to Apply for a Japan Student Visa
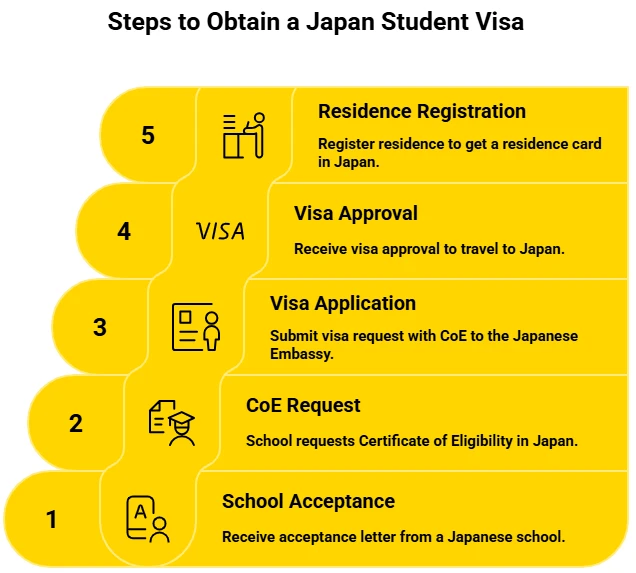
The process to apply for a Japan Student Visa is given below.
Step 1: Get accepted to a Japanese school to get your acceptance letter.
Step 2: The school then requests your Certificate of Eligibility (CoE) in Japan.
Step 3: Send your visa request along with your CoE to the Japanese Embassy in Canada.
Step 4: After visa approval, you can go to Japan.
Step 5: When you arrive, register where you live to get your residence card.
Cost of Studying in Japan
Detailed information about the cost of studying in Japan is given below.
| Expense | Estimated Cost (CAD) |
| Tuition (public university) | CAD 4,900/year |
| Tuition (private university) | CAD 7,000–15,000/year |
| Living expenses | CAD 1,200–1,800/month |
| Health insurance | CAD 300–400/year |
Japan Student Visa Fees
Detailed information about the fees for the Japan student visa is given below
| Visa Type | Fee (JPY) |
| Single-entry Visa | ¥3,000 |
| Multiple-entry Visa | ¥6,000 |
| Visa Extension | ¥4,000 |
Japan Student Visa Processing Time
Detailed information about the processing time for Japan Student Visa is given below.
| Step | Processing Time |
| Certificate of Eligibility (CoE) | 1–2 months |
| Visa application at the Embassy in Canada | 5–10 business days |
Renewal and Extension of Japan Student Visas
Japan student visas can be extended if your studies last longer than the original visa's term. It's important to apply for this extension at the local Japanese immigration office before your current visa runs out. After graduation, students can switch to a work visa if they get a job offer.
Challenges and Tips for a Successful Application
Here are some potential challenges and tips for obtaining a student visa for Japan.
| Challenge | Tip for Success |
|---|---|
| Strict financial requirements | Show clear proof of funds covering tuition and living expenses. |
| Complex documentation process | Start early and verify translations and certifications carefully. |
| CoE delays | Apply well in advance to avoid missing semester start dates. |
How Can Y-Axis Help You?
Y-Axis is a well-regarded overseas education, career, and immigration consultancy firm that supports Canadian students pursuing academic opportunities in Japan. We offer expert advice and personalized aid to simplify the entire process, from application to settling in.
Our services cover:
- Reviewing qualifications and helping select universities or courses.
- Aiding with scholarship applications and financial planning.
- Preparing documents and helping with student visa applications.
- Providing pre-departure briefings and housing advice.
- Offering support to help with settling in after arrival in Japan.
Frequently Asked Questions
